By: Virgilio C. Ventura
Filipino and Southeast Asian cuisines are renowned for their unique and vibrant flavors, often characterized by using aromatic herbs and spices. One such ingredient that plays a pivotal role in these culinary traditions is lemongrass (Cymbopogon citratus) or Tanglad to Filipinos. Often seen growing on side streets, this humble herb packs a punch in terms of both flavor and health benefits. In this article, we will explore the various ways the tanglad enhances the culinary experience in Filipino and Southeast Asian dishes, and delve into its remarkable nutritional properties.
Lemongrass Farming in the Philippines and Global Commercial Value
Tanglad grows abundantly in the Philippines as it is a native plant in the Southeast Asian region. Aside from Southeast Asia, tanglad is also commercially cultivated in mostly tropical and sub-tropical regions of India, South Africa, and other parts of the world like Turkey, France, Hungary, Italy, and Sweden.
With its long, green, and linear leaves tapering upwards and falling into the margins, the tanglad plant is commercially cultivated for the aromatic oil that is extracted from its leaves as used in the making of perfumes, soaps, detergent, cosmetics, antibacterials, and mosquito repellent products. Its leaves remain to be a major ingredient in Asian health beverage like tea and medicine to prevent headache, toothache, and stomachache.

“Though extraction of lemon grass oil has been largely a backyard or cottage industry undertaking, the Bugalods of Kalinga, through their company the Gold In Grass Corp. (GIGC) developed the distilling technology to efficiently extract the oil, said Belen Abalos, who has been at the frontline for eSearch in promoting this crop to several other places in the Cordilleras to ensure the sustainability of the industry and help the country be a net exporter of this essential oil to Japan.”1/
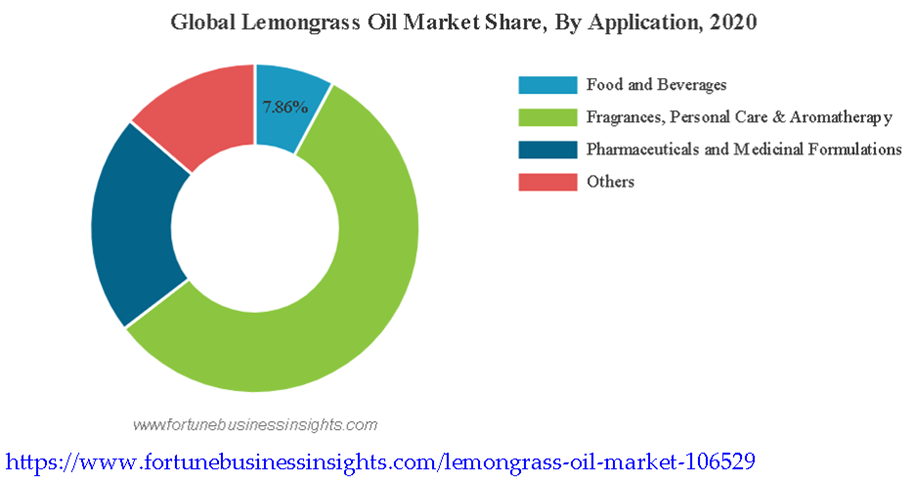
“According to projections, the industry would be worth US$ 72.9 Million by 2032, up from US$ 42.3 Million in 2022. At the end of 2021, the Lemongrass Oil Market was valued at US$ 40.2 Million. “2/
Rising awareness regarding the endless benefits of the product is the key factor driving the lemongrass market growth with Europe dominating the market in terms of revenue share in 2020. With fragrances, personal care and aromatherapy segment holding the major share in the global market, there is no doubt that the growing demand for aromatherapy is the new market trend.3/
Lemongrass in Filipino and Southeast Asian Cuisine
Flavor Profile
Citrusy Aroma: It imparts a delightful citrusy fragrance with hints of lemon, mint, and ginger to dishes. This unique aroma contributes to the complex and refreshing flavors of Filipino and Southeast Asian cuisine.
Versatile Use: It is used in various culinary applications, including soups, curries, stir-fries, marinades, and beverages, adding depth and brightness to the dishes.
Culinary Applications
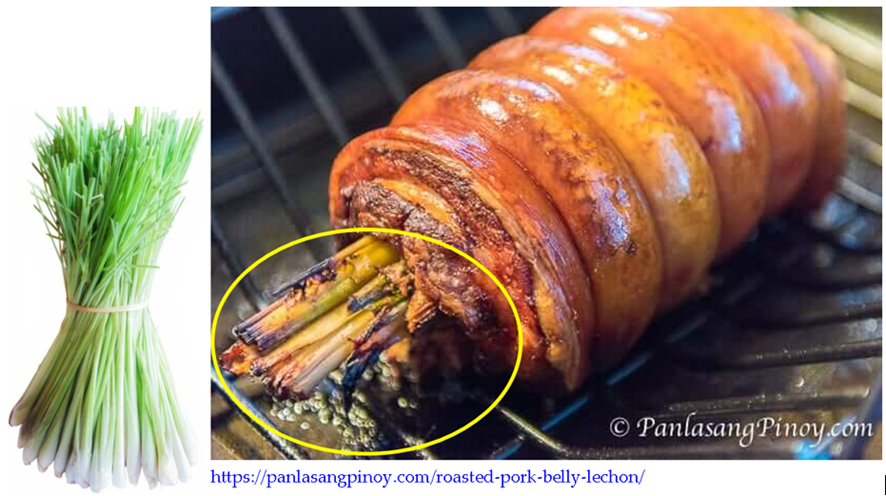
Pork and Chicken Lechon: Tanglad is a must filler inside the hog and chicken lechon belly before being roasted on top of a heap of charcoal fire. The aroma of tanglad drives away any stench from the meat and likewise adds flavor to the whole lechon.

Sinigang: In Filipino cuisine, tanglad is a key ingredient in sinigang, a sour soup known for its distinct tangy flavor. It complements the souring agents like tamarind or calamansi, balancing the dish’s taste.
Tom Yum: In Thai cuisine, lemongrass plays a prominent role in the iconic tom yum soup. Its aromatic essence combines with other herbs and spices to create a harmonious and zesty broth.
Lemongrass Tea: It is brewed into a soothing herbal tea, commonly enjoyed in Southeast Asia. It offers a calming and refreshing beverage, perfect for relaxation.
Nutritional Benefits of Lemongrass
Lemongrass is considered a quintessential food and feed additive at the industrial level since there are no issues with residue or toxins. Lemongrass powder and essential oils are used to modulate the gut ecosystem by generating anti-microbial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant responses, increasing the optimum nutrient absorption in the gut system.4/
Lemongrass is an aromatic plant with antioxidant and antimicrobial properties, used for the preparation of medicinal tea and medicinal essential oils. Previous studies have shown that extracts of lemongrass leaves contain phenolic compounds associated with health benefits.5/
The presence of high percentage of lemongrass leaves in herbal tea formulations possess good antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anti-obesity potential as an alternative to conventional medicine treatment.6/
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Citral Content: Lemongrass contains citral, a compound known for its anti-inflammatory properties. It may help reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms in conditions like arthritis (Thring et al., 2009).7/

Relief from Digestive Issues: Lemongrass tea is often used to soothe digestive discomfort, such as bloating and cramping.
Immune System Support
Vitamin C: Lemon grass is a good source of vitamin A and C. Both of those vitamins are important for immunity. Vitamin C is also known for its high levels of antioxidants.
Antimicrobial Properties: Compounds in lemongrass, such as citronellol, exhibit antimicrobial activity, helping protect against infections (Rath et al., 2014).8/
Digestive Health
Gastrointestinal Benefits: Lemongrass has been used traditionally to aid digestion, alleviate stomachaches, and reduce gastric issues (Karousou et al., 2018).9/ Lemongrass tea is an alternative remedy for upset stomach, stomach cramping, and indigestions.
Detoxification: Some studies suggest that lemongrass may support liver function and help detoxify the body (Al-Snafi, 2019).10/
Conclusion
Lemongrass is an invaluable ingredient in Filipino and Southeast Asian cuisines, contributing its unique citrusy aroma and myriad health benefits to a wide range of dishes. Thus, nutritionists and culinary experts are encouraging you to explore the world of lemongrass-infused recipes and savor the delightful flavors and nutritional advantages it offers. Whether you’re seeking to add a burst of flavor to your meals or harness its potential health benefits, lemongrass has much to offer to both your palate and your well-being. END
NOTES:
1/ Lemon Grass, Philippine Star, February 5, 2006. https://www.philstar.com/business/agriculture/2006/02/05/320141/lemon-grass
2/ Lemongrass Oil Market Outlook (2022 to 2032), Future Market Insights. https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/lemongrass-oil-market#:~:text=According%20to%20projections%2C%20the%20industry,valued%20at%20US%24%2040.2%20Million.&text=Lemongrass%20Oil%20is%20extracted%20from,the%20lemongrass%20(Cymbopogon)%20herb.
3/ Lemongrass Oil Market Size, Share & COVID-19 Impact Analysis, By Type (Pure Oil and Blend), Application (Food and Beverages, Fragrances, Personal Care and Aromatherapy (Food & Beverages, Fragrances, Personal Car & Aromatherapy, Pharmaceuticals and Medicinal Formulations, and others), and Regional Forecast, 2021-2028. Fortune Business Insights. https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/lemongrass-oil-market-106529
4/ Kiani, H. S., Ali, A., Zahra, S., Hassan, Z. U., Kubra, K. T., Azam, M., & Zahid, H. F. (2022). Phytochemical Composition and Pharmacological Potential of Lemongrass (Cymbopogon) and Impact on Gut Microbiota. AppliedChem, 2(4), 229–246. MDPI AG. Retrieved from http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem2040016 https://www.mdpi.com/2673-9623/2/4/16
5/ Kieling, D. D., & Prudencio, S. H. (2019). Blends of lemongrass derivatives and lime for the preparation of mixed beverages: antioxidant, physicochemical, and sensory properties. Journal of the science of food and agriculture, 99(3), 1302–1310. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.9305 https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1002/jsfa.9305
6/ Abdullah, R. et al. (2023), Formulation of herbal tea using Cymbopogon citratus, Foeniculum vulgare and Murraya koenigii and its anti-obesity potential. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2023.102734 1018-3647/ 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of King Saud University. This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
7/ Thring, T. S., Hili, P., & Naughton, D. P. (2009). Anti-collagenase, anti-elastase and anti-oxidant activities of extracts from 21 plants. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 9(1), 1-11. https://bmccomplementmedtherapies.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1472-6882-9-27#citeas
8/ Rath, C. C., Devi, S. S., Dash, S. K., & Mishra, R. K. (2014). Phytochemical, antimicrobial, and antioxidant studies of Cymbopogon citratus (DC.) Stapf extracts. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science, 4(10), 053-057.
9/ Karousou, R., Balta, M., & Hanlidou, E. (2018). Ethnobotanical survey of medicinal plants used in the traditional treatment of inflammatory diseases in Chios Island, Greece. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 219, 329-367.
10/ Al-Snafi, A. E. (2019). The pharmacology of Cymbopogon citratus—A review. IOSR Journal of Pharmacy, 9(1), 73-80.